Spotting The Deception: Unmasking Fake Text Messages With Black Backgrounds
In our hyper-connected world, where communication flows at the speed of light, the humble text message remains a cornerstone of daily interaction. But beneath the surface of convenience lies a growing threat: the prevalence of fake text messages, often presented with a distinctive black background, designed to deceive, manipulate, and defraud. Understanding how these deceptive messages operate is no longer just about digital savviness; it's a crucial skill for protecting your financial well-being and personal security in an increasingly complex digital landscape.
From fabricated conversations used to spread misinformation to sophisticated phishing attempts masquerading as legitimate alerts, these digital forgeries are a serious concern. This comprehensive guide will delve into the world of fake text messages, particularly those with the common black background aesthetic, equipping you with the knowledge and tools to identify, avoid, and combat these pervasive digital threats. We'll explore their anatomy, the motivations behind their creation, and most importantly, how you can safeguard yourself against their harmful intentions.
Table of Contents
- 1. The Rise of Digital Deception: Understanding Fake Text Messages
- 2. The "Black Background" Aesthetic: A Visual Cue of Fabrication
- 3. Anatomy of a Fake Text Message: What to Look For
- 4. The Role of AI in Fabricating Digital Interactions
- 5. Common Scenarios Involving Fake Text Messages
- 6. Protecting Yourself: Practical Steps Against Fake Text Messages
- 7. The Broader Impact: Why Digital Literacy Matters
- 8. Navigating the Digital Landscape with Confidence
1. The Rise of Digital Deception: Understanding Fake Text Messages
The digital age, while bringing unprecedented connectivity, has also ushered in an era of sophisticated deception. Fake text messages are a prime example of this, representing a pervasive form of digital fraud and manipulation. At their core, fake text messages are fabricated conversations or alerts designed to appear authentic, but which are entirely artificial. They can be simple pranks, but more often, they are tools for malicious intent, ranging from spreading misinformation to executing elaborate financial scams.
These messages are created using various tools, from basic screenshot manipulation to advanced text generation software. Their purpose is to elicit a specific reaction from the recipient – be it fear, urgency, curiosity, or trust – to achieve a nefarious goal. The motivations behind creating these messages are diverse: some aim to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information, others seek to spread false narratives, and some are simply designed to cause confusion or embarrassment. The danger lies in their ability to mimic legitimate communication, making them difficult for the untrained eye to distinguish from the real thing.
2. The "Black Background" Aesthetic: A Visual Cue of Fabrication
One common visual characteristic of many circulated fake text message screenshots is a dark or black background. This isn't just a stylistic choice; it often serves a practical purpose for those creating the fakes. Many modern messaging applications offer a "dark mode" or themes with black backgrounds, which can make text easier to read in low light and reduce eye strain. When someone creates a fake text message screenshot, choosing a black background can make it appear more contemporary and, ironically, more "authentic" to a tech-savvy audience accustomed to dark mode interfaces.
Furthermore, a black background can make text, especially white or light-colored text, stand out more prominently, drawing immediate attention to the fabricated conversation. This visual clarity can be crucial when the goal is to quickly convey a false narrative or a sense of urgency. While not every text message with a black background is fake, and many legitimate conversations happen on dark mode, its frequent use in fabricated content makes it a visual cue worth noting. It often indicates that the image is a screenshot, which, while not inherently suspicious, opens the door to potential manipulation outside of a live, verifiable chat.
3. Anatomy of a Fake Text Message: What to Look For
Discerning a genuine message from a fake text message black background screenshot requires a keen eye and an understanding of common deceptive tactics. Here are key elements to scrutinize:
- Grammar and Spelling Errors: Legitimate organizations and individuals typically proofread their communications. Frequent typos, awkward phrasing, or grammatical mistakes are significant red flags. Scammers, especially those operating from non-English speaking regions, often overlook these details.
- Unusual Sender Information: Does the sender's number look strange? Is it a generic mobile number when it should be a short code or an official company name? Fraudsters often use burner phones or spoofed numbers. Be wary of messages claiming to be from banks, government agencies, or well-known companies that come from an unidentifiable or personal-looking number.
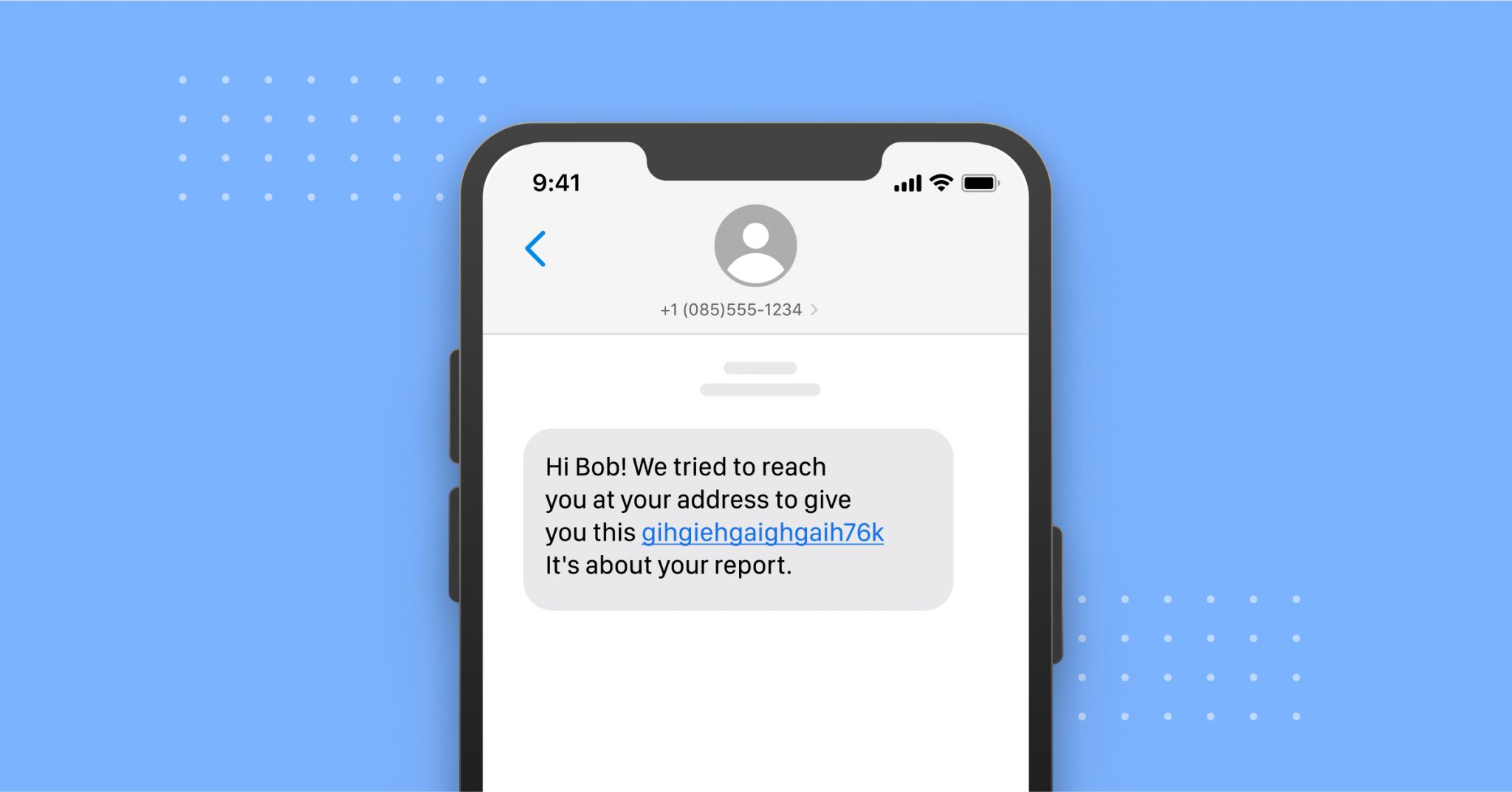
- Urgency and Threats: Fake messages frequently employ high-pressure tactics. Phrases like "Immediate action required," "Your account will be suspended in 24 hours," or "Failure to respond will result in charges" are designed to bypass critical thinking and provoke an immediate, unverified response. This sense of urgency is a classic hallmark of phishing and scam attempts.
- Requests for Personal Information: Any text message asking for sensitive data like your full name, address, Social Security Number, bank account details, credit card numbers, or passwords should be treated with extreme suspicion. Legitimate entities rarely request such information via unsolicited text messages. This directly relates to YMYL principles, as sharing this data can lead to identity theft or financial ruin.
- Suspicious Links (Phishing): A common tactic is to include a link that looks legitimate but directs you to a fake website designed to steal your credentials. Hover over links (if on a computer) or long-press them (on mobile, without clicking) to see the actual URL. Look for subtle misspellings (e.g., "Amaz0n" instead of "Amazon"), extra characters, or unusual domain extensions. Even if the link seems related to a known entity, it could be a sophisticated phishing attempt.
- Unsolicited Messages: If you haven't initiated contact or aren't expecting a message from a particular entity, be extra cautious. For example, a text from a bank about an issue you weren't aware of, or a delivery notification for a package you didn't order, warrants skepticism.
- Inconsistent Information: Does the message contradict information you already know? For instance, if a text claims your bank account is frozen, but you just used your card, it's likely a fake.
4. The Role of AI in Fabricating Digital Interactions
The landscape of digital deception is rapidly evolving, and a significant driver of this change is the advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AI). AI's capability to generate highly convincing content has profound implications for the creation and detection of fake text messages, particularly those with a black background, making the line between real and fabricated increasingly blurry. While AI has been widely discussed for its role in creating deepfake videos and audio, its application in generating realistic text is equally, if not more, insidious for everyday communication.
4.1. AI-Generated Content: Beyond Audio and Video
The "Data Kalimat" provided examples like "Áudio foi criado com inteligência artificial" (Audio was created with artificial intelligence) and "Vídeo foi criado com ia post que viralizou criou falas que não foram" (Video was created with AI, viral post created speeches that weren't real), along with "gravação foi adulterada com inteligência artificial" (recording was adulterated with artificial intelligence). These instances highlight AI's power to mimic human expression and manipulate digital media. This same technology is now being leveraged to craft incredibly persuasive fake text messages.
Large Language Models (LLMs) can generate text that is grammatically perfect, contextually relevant, and even mimics specific writing styles. This means an AI can be prompted to create an entire fake conversation between two individuals, complete with natural dialogue, emotional nuances, and even specific slang or jargon. Imagine an AI generating a fake text message black background conversation that appears to be from a friend asking for money, or a convincing exchange with a customer service representative designed to trick you into revealing personal details. The ability of AI to produce such sophisticated text makes it incredibly difficult for human recipients to detect the fabrication based on linguistic cues alone.
Furthermore, AI can be used to automate the creation of countless variations of phishing messages, making it harder for spam filters to catch them. It can adapt to different contexts, impersonate various entities, and even personalize messages based on publicly available information, increasing their success rate. The challenge now isn't just spotting obvious errors, but recognizing the subtle signs of artificiality in seemingly flawless communication. This necessitates a shift in our approach to digital literacy, moving beyond simple checks to a more holistic skepticism about unsolicited digital interactions.
5. Common Scenarios Involving Fake Text Messages
Fake text messages, especially those circulated as screenshots with a black background, are employed in a myriad of deceptive scenarios. Understanding these common applications is crucial for recognizing and avoiding their traps. Many of these scenarios directly impact your financial stability and personal safety, making them prime examples of YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) concerns.
5.1. Financial Scams and Phishing Attempts
A significant portion of fake text messages are designed to extract money or sensitive financial information. The "Data Kalimat" mentions examples like "É #fake anúncio que manipula vídeo do g1 e exige pix para devolver dinheiro de vítimas de fraude no inss" (It's a fake ad that manipulates a G1 video and demands Pix to return money to INSS fraud victims) and "É #fake página que imita a globo.com e diz que luiza trajano recomenda plataforma de criptomoedas" (It's a fake page that imitates globo.com and says Luiza Trajano recommends a cryptocurrency platform). These illustrate how scammers leverage trusted brands and public figures to lure victims.
Similarly, fake text messages often impersonate banks, credit card companies, government agencies (like the tax office or social security), or even popular online retailers. They might claim there's a suspicious transaction on your account, an overdue bill, or an issue with a delivery. The message will typically include a link to a fake login page designed to steal your credentials. Other variants include fake "sweepstakes" winnings that require a small fee (a "Pix" payment, as mentioned in the data) to release a larger sum, or "investment opportunities" promising unrealistic returns, often linked to fake cryptocurrency platforms. The mention of "jogo do tigrinho" (tiger game) also points to a common scam involving deceptive online games or betting platforms that promise easy money but are designed to defraud users.
5.2. Impersonation and Misinformation Campaigns
Beyond financial gain, fake text messages are powerful tools for spreading false information or impersonating individuals and organizations. The "Data Kalimat" provides several relevant examples: "É #fake anúncio que imita o g1 e divulga feirão limpa nome da serasa com 99% de desconto" (It's a fake ad that imitates G1 and promotes a Serasa debt forgiveness fair with 99% discount), "É #fake vídeo com padre fábio de melo pedindo doações para criança hospitalizada" (It's a fake video with Padre Fábio de Melo asking for donations for a hospitalized child), and "O fato ou fake desmentiu um falso tsunami no uruguai" (Fato ou Fake debunked a false tsunami in Uruguay).
These show how trusted news sources (G1), respected public figures (Padre Fábio de Melo), and even natural disasters can be manipulated to create convincing but false narratives. Fake text messages can serve as the initial vector for these hoaxes, circulating fabricated conversations or alerts that appear to come from official channels or credible individuals. They might contain sensational claims, political propaganda, health misinformation, or even personal attacks designed to damage reputations. For instance, a fake text message black background screenshot could show a fabricated conversation between public figures discussing a scandal, or an "official" alert about a non-existent emergency, causing widespread panic or confusion. The objective here is not always direct financial gain, but rather to influence public opinion, sow discord, or simply create chaos.
5.3. Personal Attacks and Reputation Damage
Fake text messages are also weaponized in personal disputes, bullying, or to damage someone's reputation. The "Data Kalimat" hints at this with examples like "É #fake que zé felipe disse ter se separado de virginia porque não queria mais divulgar 'jogo do tigrinho'" (It's fake that Zé Felipe said he separated from Virginia because he no longer wanted to promote 'jogo do tigrinho') and "Procurada pelo fato ou fake, a assessoria de imprensa de virginia informou que a influenciadora não teve qualquer contato recente com rodrigo lombardi" (Contacted by Fato ou Fake, Virginia's press office informed that the influencer had no recent contact with Rodrigo Lombardi). These show how fabricated narratives, often involving celebrities, can be created and spread, impacting their public image.
On a personal level, individuals might create fake text message black background conversations to falsely accuse someone, spread rumors, or present a misleading version of events. These fabricated chats can be used as "evidence" in arguments, legal disputes, or simply to defame someone among their social circle. The visual nature of a screenshot makes it appear tangible and verifiable, even if the content is entirely manufactured. This form of digital manipulation can have severe emotional, social, and even professional consequences for the victims, underscoring the critical need for vigilance and fact-checking.
6. Protecting Yourself: Practical Steps Against Fake Text Messages
Given the sophistication of fake text messages, especially those using a black background aesthetic, a proactive approach to digital security is essential. Here are practical steps you can take to protect yourself and your loved ones:
- Verify Sender Identity Independently: If a message, particularly one with a sense of urgency or requesting action, claims to be from a bank, government agency, or company, do not respond directly or click any links. Instead, contact the organization using a phone number or email address you know to be legitimate (e.g., from their official website or a previous statement). Never use contact details provided in the suspicious message itself.
- Never Click Suspicious Links: This is perhaps the most critical rule. Phishing links are designed to steal your credentials or install malware. Even if the link looks somewhat legitimate, the risk is too high. If you believe a message might be real, navigate directly to the official website of the organization in question through your browser, rather than clicking a link in a text.
- Do Not Share Personal or Financial Information: Legitimate organizations will almost never ask for sensitive data like passwords, PINs, or full credit card numbers via text message. Be extremely wary of any such requests. Your Money or Your Life principles dictate that protecting this information is paramount to your financial security.
- Report and Block: Most smartphones allow you to report spam or block numbers. Reporting helps your carrier identify and block similar scams, while blocking prevents the specific sender from contacting you again. Forward suspicious texts to your carrier's spam reporting number (e.g., 7726 in the US and Canada).
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): For all your online accounts, especially financial ones, enable 2FA. This adds an extra layer of security, requiring a second verification step (like a code sent to your phone) even if a scammer manages to get your password.
- Be Skeptical of Offers That Seem Too Good to Be True: As seen with the "99% discount" or "cheap phone auction" examples in the "Data Kalimat," scammers often lure victims with irresistible deals. If an offer seems unbelievably generous, it's almost certainly a scam.
- Educate Yourself and Others: Stay informed about the latest scam tactics. Share information with friends and family, especially those who might be less tech-savvy. A collective awareness is our best defense.
- Review Screenshots Critically: If you see a fake text message black background screenshot circulating online, apply the same critical thinking. Look for inconsistencies, grammatical errors, and unnatural dialogue. Consider the source of the screenshot and its potential motives.
7. The Broader Impact: Why Digital Literacy Matters
The proliferation of fake text messages and other forms of digital deception, including those with a fake text message black background, underscores a fundamental challenge of our modern age: the erosion of trust in digital information. When fabricated content can spread rapidly and convincingly, it not only impacts individuals but also has broader societal implications. The "Fato ou Fake" initiative, mentioned in the "Data Kalimat" as debunking various falsehoods from fake websites imitating official ones to manipulated celebrity content, highlights the critical need for dedicated fact-checking and public awareness campaigns.
A society where people struggle to distinguish truth from fabrication is vulnerable to misinformation, panic, and exploitation. It can undermine public trust in institutions, influence elections, and even incite real-world harm. The ability of AI to generate increasingly realistic fake content means that the responsibility to critically evaluate information falls more heavily on each individual. Digital literacy, therefore, is no longer an optional skill but a civic imperative. It encompasses not just knowing how to use technology, but understanding its potential for manipulation, recognizing the signs of deception, and actively seeking out verified information from authoritative sources. By fostering a culture of healthy skepticism and critical thinking, we can collectively build a more resilient digital environment, one where the power of deception is significantly diminished.
8. Navigating the Digital Landscape with Confidence
The digital world, with all its conveniences and opportunities, also presents a complex array of threats, among them the insidious nature of fake text messages, often disguised with a sleek black background. As we've explored, these messages are not mere annoyances; they are sophisticated tools of fraud, misinformation, and personal attack, designed to exploit trust and vulnerability. From phishing attempts that target your financial security to fabricated narratives that sow discord, the stakes are undeniably high, touching upon the core principles of Your Money or Your Life.
However, by understanding the anatomy of these deceptions, recognizing the tell-tale signs, and adopting proactive security measures, you can significantly reduce your risk. Remember to always verify, never rush, and be inherently skeptical of unsolicited communications, especially those demanding immediate action or personal information. Embrace digital literacy as a continuous journey, staying informed about evolving threats and sharing your knowledge with others. In a world where digital interactions increasingly shape our realities, your vigilance and informed decisions are your strongest defenses. Stay safe, stay smart, and navigate the digital landscape with the confidence that comes from being well-prepared.
What are your thoughts on identifying fake text messages? Have you ever encountered a particularly convincing fake text message black background scam? Share your experiences and tips in the comments below to help our community stay safe!
How to identify a fake text message? | Birdeye
Text bubbles - Apple Community
Blank Imessage Template Dark Mode - prntbl.concejomunicipaldechinu.gov.co