Mastering Key Management: Your Digital Security Fortress
Table of Contents
- What is Key Management and Why Does It Matter?
- The Core Pillars of Effective Key Management
- Navigating Recovery Keys and Trusted Devices
- The Human Element in Key Management: User Responsibility and Challenges
- Best Practices for Personal Key Management
- Key Management in the Enterprise: Scaling Security
- Future Trends in Key Management
- Conclusion: Your Role in a Secure Digital Future
What is Key Management and Why Does It Matter?
At its heart, **key management** refers to the entire lifecycle of cryptographic keys. Think of these keys as unique, complex sequences of data that are essential for encryption, decryption, and digital authentication. Just as a physical key grants access to your home or car, a digital key grants access to your data, your accounts, and your identity online. Without proper key management, even the strongest encryption algorithms are rendered useless if the keys themselves are compromised, lost, or mishandled. Why does this matter to you? Because every time you log into an online banking portal, send a secure email, or even just browse a website with "https" in its address, cryptographic keys are silently working in the background. They ensure that your communications are private, your transactions are secure, and your identity is verified. If these keys are not managed effectively, the integrity of your personal information, your financial security (Your Money), and even your safety (Your Life, in cases of sensitive personal data exposure) are at risk. A breach in key management can lead to devastating consequences, from financial fraud and identity theft to the complete loss of access to your digital assets. This is precisely why key management falls squarely under the YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) criteria, demanding the highest level of expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness in its discussion.The Core Pillars of Effective Key Management
Effective **key management** isn't a single action but a continuous process encompassing several critical stages. Each stage is vital for maintaining the security and integrity of your digital keys.Generation and Storage: The Birth of a Key
The journey of a key begins with its generation. For a key to be truly secure, it must be generated in a way that is unpredictable and random, making it impossible for anyone to guess or reproduce. This often involves complex algorithms and hardware-based random number generators to ensure cryptographic strength. Once generated, the paramount concern becomes secure storage. Consider a recovery key, like those used for Apple IDs. The advice is clear: "Write down your recovery key and keep it in a safe place." This seemingly simple instruction underscores a fundamental principle: a key, regardless of its digital nature, often requires a physical, offline backup. Storing keys securely means protecting them from unauthorized access, loss, or damage. For individuals, this might involve using a password manager, an encrypted drive, or even a physical safe for written recovery keys. For organizations, it scales up to specialized hardware security modules (HSMs) or dedicated key management systems (KMS) that provide tamper-resistant environments for key storage. The goal is always to ensure that the key is accessible only to authorized entities and remains uncompromised throughout its lifespan.Distribution and Usage: Keys in Action
Once a key is generated and securely stored, it needs to be distributed to the entities that will use it. This distribution must also be secure, preventing interception or compromise during transit. For instance, when you establish a secure connection to a website, your browser and the website's server exchange cryptographic keys in a carefully orchestrated handshake, ensuring that the session is encrypted from end to end. The usage phase is where keys perform their primary functions: encrypting data, decrypting information, and authenticating identities. Every time you unlock your phone with a passcode, sign into an app with multi-factor authentication, or send an encrypted message, keys are actively being used. The principle here is "least privilege" – keys should only be used for their intended purpose and by authorized users, for the shortest possible duration. This minimizes the window of opportunity for potential compromise.Rotation and Revocation: Maintaining Security Over Time
Keys, like physical locks, can wear out or become compromised over time. Key rotation involves periodically replacing old keys with new ones. This practice limits the amount of data encrypted with a single key, reducing the impact if that key were ever compromised. It's like changing the locks on your house every so often, even if there hasn't been a break-in. Key revocation, on the other hand, is a critical emergency measure. If a key is suspected of being compromised, lost, or no longer needed (e.g., an employee leaves an organization), it must be immediately revoked. Revocation renders the key unusable, preventing any further unauthorized access or decryption. The "Data Kalimat" provided an excellent example: "Remove the device you no longer wish to use to verify your identity." This directly relates to revoking the trust associated with a device's key, preventing it from being used for authentication. This proactive measure is vital in limiting potential damage from a security incident.Navigating Recovery Keys and Trusted Devices
The concept of a recovery key is a powerful illustration of advanced **key management** in personal security. Services like Apple ID offer recovery keys as an enhanced security measure, going beyond traditional password-based account recovery. The statement, "Using a recovery key is more secure, but it means that you’re responsible," perfectly encapsulates the trade-off. While it provides a stronger layer of protection against unauthorized access, it shifts the burden of safekeeping entirely to the user. Consider the scenario: "If you generated a recovery key, you can't use account recovery." This highlights a critical design choice. By opting for a recovery key, you're explicitly choosing a higher security posture that bypasses standard recovery mechanisms. This means if you lose your recovery key and forget your Apple ID password, you might lose access to your account permanently. However, the system often provides alternatives. The data states, "As long as you remember your apple id password and still have access to one of your trusted devices, you can sign in and create a new recovery." This demonstrates a multi-layered approach to account access and recovery, where a combination of your password and a trusted device can act as a fallback, even if the recovery key is lost. To set up or manage such a key, you might "Tap recovery key, turn on recovery key, then tap use recovery key and enter your device passcode." This process binds the recovery key to your device and requires your device passcode, adding another layer of authentication. Furthermore, the system often has specific requirements: "Make sure the device is running ios 11 or macos high sierra or later." This ensures that the underlying operating system supports the necessary cryptographic functions and security protocols for robust key management. The interplay between your password, trusted devices, and the recovery key forms a sophisticated personal key management system, emphasizing both convenience and security, but always with the caveat of user responsibility.The Human Element in Key Management: User Responsibility and Challenges
While cryptographic algorithms and sophisticated systems form the backbone of **key management**, the human element remains the most significant variable, and often, the weakest link. User responsibility is paramount. As the data suggests, "Using a recovery key is more secure, but it means that you’re responsible." This responsibility extends to remembering passwords, securely storing recovery keys, and maintaining the integrity of trusted devices. One common challenge users face is simply forgetting keys or passwords. This is a primary reason why recovery mechanisms exist. The ideal scenario is that "As long as you remember your apple id password and still have access to one of your trusted devices, you can sign in and create a new recovery." This highlights how a combination of factors can help overcome a single point of failure (like a forgotten recovery key). Beyond memory, practical user interface issues can also pose subtle challenges to effective key management. The provided data mentions, "The location of backslash (and any letter, symbol etc.) depends on the active keyboard layout," and "Keys on a macbook pro when i push some of my keys, they type double the letter, especially on one side of my keyboard." While seemingly minor, these details underscore how the physical act of entering a key or password can be fraught with errors. Incorrect keyboard layouts, sticky keys, or even the subtle differences in how a "delete" key functions ("The delete key opn mac does and doesn't act the same way as the backspace and delete keys on a pc,Normally hitting delete on a mac will work as a backspace key") can lead to frustrating login attempts, password resets, or even accidental data loss. These seemingly trivial issues can disrupt workflows and, in a worst-case scenario, lead users to adopt less secure practices out of frustration. Furthermore, managing trusted devices requires vigilance. You might need to "Remove the device you no longer wish to use to verify your identity" if it's lost, sold, or no longer in use. Failing to do so leaves a potential backdoor into your accounts. The human factor also involves understanding system requirements: "Make sure the device is running ios 11 or macos high sierra or later" ensures that the security features you rely on are actually supported and functioning correctly on your hardware. Ultimately, even the most robust key management system relies on informed, responsible user behavior to be truly effective.Best Practices for Personal Key Management
For individuals, effective **key management** boils down to a few actionable best practices that significantly enhance your digital security posture: * **Strong, Unique Passwords:** This is the foundational layer. Use a password manager to generate and store complex, unique passwords for every online account. Never reuse passwords. * **Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):** Whenever possible, enable MFA. This adds a second layer of verification, often through a code sent to a trusted device or an authenticator app. Even if your password is stolen, an attacker can't access your account without this second factor. * **Secure Recovery Key Storage:** If a service offers a recovery key, take it seriously. "Write down your recovery key and keep it in a safe place." This safe place should be offline and physically secure, like a fireproof safe or a secure deposit box. Do not store it digitally on a device that could be lost or compromised. Remember, if you use a recovery key, "you’re responsible" for its safekeeping. * **Manage Trusted Devices:** Regularly review the list of trusted devices associated with your accounts. If you sell, lose, or no longer use a device, "Remove the device you no longer wish to use to verify your identity." This prevents unauthorized access through old, unmonitored devices. * **Understand Account Recovery Options:** Familiarize yourself with how to recover access to your accounts. Know the difference between using a recovery key, a trusted phone number, or standard account recovery processes. Be aware of the implications: "If you generated a recovery key, you can't use account recovery" through traditional means. * **Keep Software Updated:** Ensure your devices are running the latest operating systems ("Make sure the device is running ios 11 or macos high sierra or later"). Updates often include critical security patches that address vulnerabilities in how keys are handled or protected. * **Be Mindful of Input:** While seemingly minor, be aware of your keyboard layout and potential input issues when entering sensitive information. Double-check passwords and recovery keys for accuracy. Activating a "keyboard viewer" (as mentioned in the data) can be helpful in identifying character locations, especially for unusual symbols in complex keys.Key Management in the Enterprise: Scaling Security
While the principles of **key management** remain consistent, their implementation scales significantly in an enterprise environment. Businesses deal with vast numbers of keys, protecting everything from customer data and intellectual property to internal communications and critical infrastructure. The stakes are incredibly high, often impacting "Your Money" (financial stability, legal penalties) and "Your Life" (customer privacy, operational continuity). Enterprise key management systems (KMS) are sophisticated platforms designed to automate and enforce the entire key lifecycle. They often integrate with Hardware Security Modules (HSMs), which are specialized physical devices that provide a highly secure, tamper-resistant environment for generating, storing, and managing cryptographic keys. HSMs are the gold standard for enterprise key security, ensuring that keys are never exposed to less secure software environments. Businesses must also contend with regulatory compliance (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS), which often mandates specific key management practices. This includes strict access controls, comprehensive auditing of key usage, and robust key rotation and revocation policies. Cloud environments introduce additional complexities, requiring cloud-native key management services that integrate seamlessly with cloud infrastructure while maintaining enterprise-level security and control. The goal is to achieve centralized control, automation, and visibility over all keys across the organization, minimizing human error and maximizing security.Future Trends in Key Management
The landscape of **key management** is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in computing power, new cryptographic challenges, and emerging technologies. One of the most significant upcoming challenges is **quantum computing**. Current encryption methods, which rely on the computational difficulty of factoring large numbers, could theoretically be broken by powerful quantum computers. This has led to intense research in **post-quantum cryptography (PQC)**, which aims to develop new algorithms that are resistant to quantum attacks. Future key management systems will need to incorporate these new PQC algorithms, requiring a massive shift in how keys are generated, distributed, and used. Another trend is the increasing adoption of **confidential computing**, where data remains encrypted even while being processed in memory. This requires new approaches to key management, as keys must be securely provisioned and managed within these isolated execution environments. Furthermore, the rise of **blockchain and distributed ledger technologies** introduces novel key management challenges and opportunities. Managing private keys for cryptocurrency wallets or decentralized applications requires extreme care, as their loss can mean irreversible financial loss. Innovations in multi-party computation (MPC) and threshold cryptography are emerging to distribute key ownership and reduce single points of failure in these decentralized systems. These trends highlight a future where key management becomes even more complex, automated, and critical, requiring continuous adaptation and innovation to stay ahead of evolving threats.Conclusion: Your Role in a Secure Digital Future
**Key management** is not just a technical discipline for experts; it's a fundamental aspect of digital literacy for everyone. From safeguarding your personal recovery key to understanding the importance of trusted devices, your active participation in managing your digital keys is paramount to your online safety and financial well-being. The seemingly minor details, like understanding keyboard layouts or ensuring your device runs the latest OS, contribute to the overall strength of your digital security. By embracing the principles of secure key generation, storage, rotation, and revocation, and by taking personal responsibility for your digital assets, you become an active participant in building a more secure digital future. Don't leave your digital life to chance. Take the time to review your account security settings, understand your recovery options, and implement the best practices discussed here. Your data, your money, and your peace of mind depend on it. What steps will you take today to strengthen your personal key management? Share your thoughts and questions in the comments below, and let's continue the conversation about building a safer digital world together. If you found this article helpful, consider sharing it with friends and family who might also benefit from understanding the power of effective key management.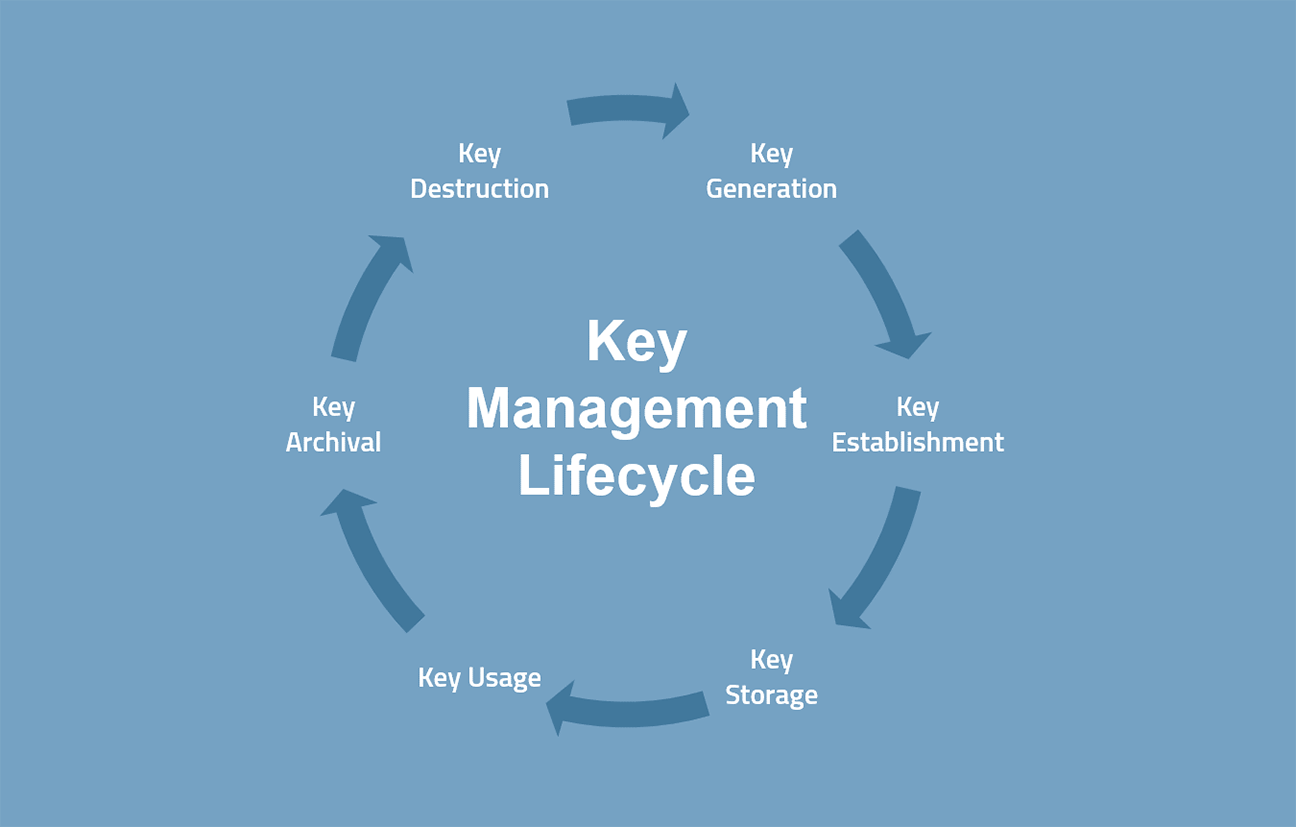
Enterprise Key Management for all cryptographic keys

What is Key Management? How does Key Management work?

What is a Key Management System? Everything You Need to Know